Introduction to Frost Heaving
Frost heaving refers to the upward movement of the ground surface caused by the formation of ice lenses in the soil. This occurs when moisture in the soil freezes, expands, and pushes the soil and any structures above it upward. In cold storage facilities, where temperatures are maintained well below freezing, this phenomenon poses a serious risk to the building’s integrity. The cold air from the storage area can penetrate through the floor insulation into the subsoil, leading to unintended permafrost formation and subsequent heaving. This can result in cracked floors, distorted foundations, and operational disruptions, potentially endangering workers and inventory.
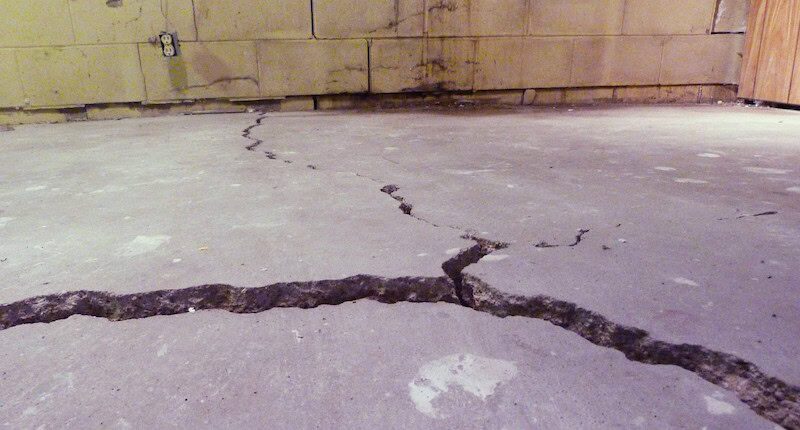

Causes of Frost Heaving in Cold Storage
For frost heaving to occur in cold storage settings, several key conditions must align:
• Freezing Soil Temperatures: The subsoil temperature must drop below 32°F (0°C), often due to heat loss from the refrigerated space through the floor slab. Even with insulation, cold leakage can happen over time, especially in facilities operating at -20°C to -30°C.
• Availability of Moisture: A continuous water source is essential, such as a high water table (within 20 feet of the surface) or surface water infiltration from rain around the building. Capillary action draws this water to the freezing front, where it forms expanding ice lenses.
• Frost-Susceptible Soil Types: Soils high in silt, loam, clay, or fine particles promote water migration and ice formation. Coarser soils like gravel or sand are less prone to this issue.
• Presence of a Slab or Structure: The rigid concrete floor acts as a surface for the ice to push against, amplifying the damage.
In cold storage, thermal bridging through foundations, pipes, or inadequate insulation accelerates the process, potentially freezing soil several meters deep. Over months or years, this slow buildup can displace floors by inches to feet, leading to cracks and structural failures.

Cases of Frost Heaving in Cold Storage in India
While specific documented cases of frost heaving in Indian cold storage facilities are limited in public records, the risk is particularly relevant in colder regions such as the Himalayan areas. In the cold arid Leh-Ladakh region, natural frost heaves have been observed causing morphological variability in landforms and contributing to pastureland degradation. This environmental phenomenon highlights the vulnerability of frost-susceptible soils in high-altitude, low-temperature zones where cold storage units for perishable goods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy are increasingly common.
India’s expanding cold chain infrastructure, especially in northern states like Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand, faces similar challenges due to seasonal freezing and variable soil moisture. Although direct incidents in commercial cold storages are not widely reported—possibly due to underreporting or preventive measures—the potential for damage is evident from global parallels and local geological studies. For instance, in areas with silty soils and high groundwater, unchecked cold leakage could mirror issues seen in older facilities elsewhere, leading to floor heaving and operational halts.
Prevention Measures for Infrastructure Owners
Infrastructure owners can mitigate frost heaving through proactive design, maintenance, and retrofitting strategies. The goal is to prevent subsoil freezing by managing heat loss and moisture:
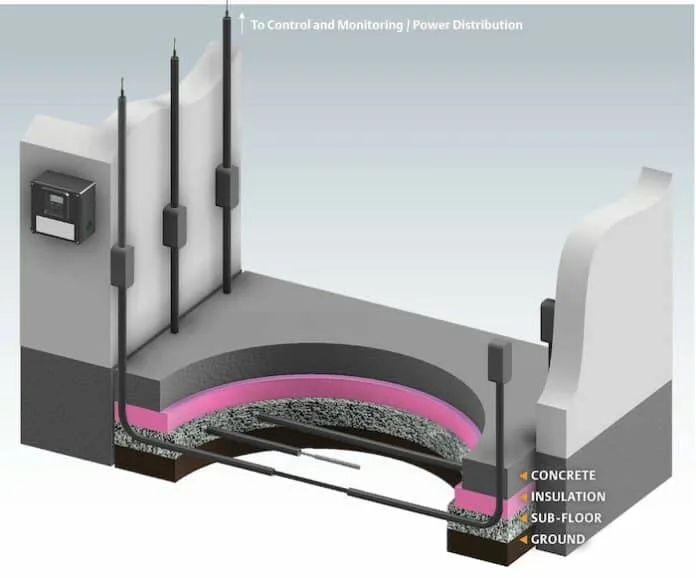
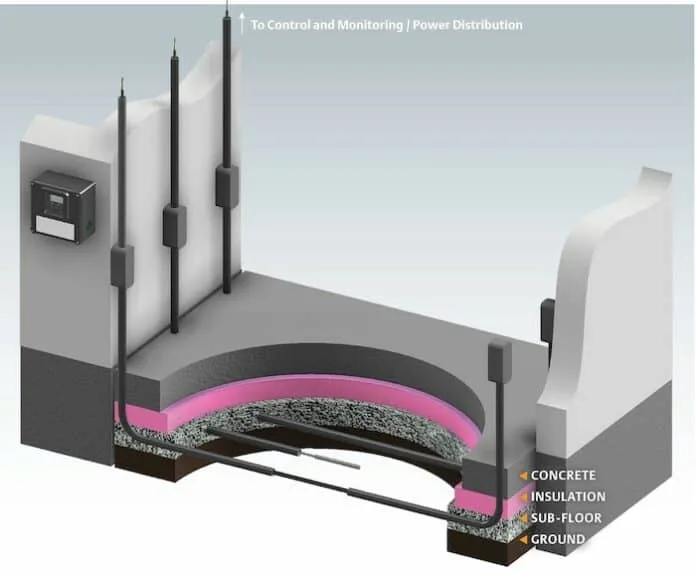
• Under-Floor Heating Systems: Install electric heating cables or mineral-insulated (MI) cables beneath the slab to maintain soil temperatures above freezing. These systems, often embedded in conduits, provide 2-4 Btu/hr-ft² of heat and can be controlled via sensors. This is a reliable, energy-efficient method for both new builds and repairs.
• Enhanced Insulation: Use high-quality, moisture-impermeable insulation under the floor slab, tapering near edges to reduce heat loss. Combining insulation with heating can minimize the depth of frost penetration.
• Ventilated Crawl Spaces: Create voids under the floor using formworks like modular systems to allow air circulation, preventing moisture buildup and cold transfer.
• Site Selection and Soil Management: Choose sites with non-frost-susceptible soils (e.g., gravel) or replace subsoil if necessary. Ensure proper drainage to lower the water table and prevent surface water infiltration.
• Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Install temperature sensors in the subsoil and conduct periodic inspections for cracks or uneven floors. Early detection allows for timely interventions, such as glycol-based heating or ambient heat utilization.
Implementing these measures not only prevents costly repairs but also ensures compliance with safety standards, protecting assets in India’s growing cold storage sector.
Conclusion
Frost heaving in cold storage facilities is a preventable yet potentially destructive issue driven by freezing soil, moisture, and susceptible geology. In India, while specific cases are underdocumented, the risk in colder regions underscores the need for vigilant prevention. By adopting heating, insulation, and monitoring strategies, infrastructure owners can safeguard their operations against this hidden threat, ensuring long-term stability and efficiency.
Sources
1. [PDF] Cold Storage Facility Design Solutions: Prevention of Frost Heave … – https://www.delta-therm.com/delta-therm.com/media/Documents/Case%20Studies/Cold-Storage-Frost-Heave-Prevention-paper.pdf
2. Preventing Frost Heave In Cold Storage Facilities | Building Envelope – https://facilityexecutive.com/preventing-frost-heave-in-cold-storage-facilities
3. Frost heave prevention system – Danfoss – https://www.danfoss.com/en-in/products/dhs/floor-heating-ice-and-snow-melting/ice-and-snow-melting-frost-protection/frost-heave-prevention-system
4. Avoid Frost Heave Damage in Cold Storage Facilities with Modern … – https://blog.chemelex.com/avoid-frost-heave-damage-in-cold-storage-facilities-with-electric-heat-tracing
5. [PDF] understanding & preventing frost heave in refrigerated facilities – https://irc.wisc.edu/export.php?ID=262
6. Freezing Damage to Tunnels in Cold Regions and Weights of … – https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/21/14637
7. [PDF] Freezer Floor Heaving And Solution – www .ec -undp – https://ec-undp-electoralassistance.org/HomePages/Resources/1kVmcF/FreezerFloorHeavingAndSolution.pdf
8. Safety in Cold Storage Warehousing and Logistics – Indicold – https://www.indicold.com/2023/07/27/ensuring-safety-in-the-cold-storage-industry-in-india-challenges-measures-and-real-world-perspectives
9. Geoplast Modulo: Frost-heaving protection for cold-storage rooms – https://www.geoplastglobal.com/en/blog/geoplast-modulo-frost-heaving-protection-for-cold-storage-rooms
10. Ensuring Safety in the Cold Storages in India – LinkedIn – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/ensuring-safety-cold-storages-india-challenges-measures-real-world